By: Amina Rangoonwala1 , Cathleen E. Jones2 , and Elijah Ramsey III1
1 U.S. Geological Survey, Wetland and Aquatic Research Center, Lafayette, Louisiana, USA, 2 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA
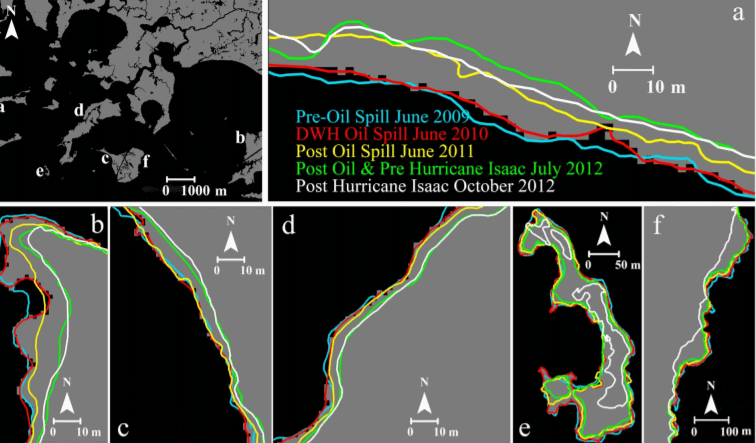
We evaluate the relative impact of petroleum spill and storm surge on near-shore wetland loss by quantifying the lateral movement of coastal shores in upper Barataria Bay, Louisiana (USA), between June 2009 and October 2012, a study period that extends from the year prior to the Deepwater Horizon spill to 2.5 years following the spill. We document a distinctly different pattern of shoreline loss in the 2 years following the spill, both from that observed in the year prior to the spill, during which there was no major cyclonic storm, and from change related to Hurricane Isaac, which made landfall in August 2012. Shoreline erosion following oiling was far more spatially extensive and included loss in areas protected from wave-induced erosion. We conclude that petroleum exposure can substantially increase shoreline recession particularly in areas protected from storm-induced degradation and disproportionally alters small oil-exposed barrier islands relative to natural erosion.
